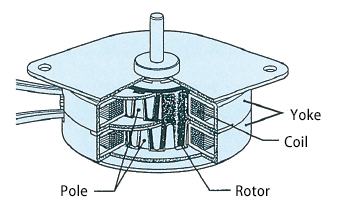
 Excitation is the process of electro-magnetizing a pole by applying electric current to the coil of a motor. There are two sets of motor coil, A-phase coil and B-phase coil, and each of them corresponds two poles: positive pole and negative pole. *1
Excitation is the process of electro-magnetizing a pole by applying electric current to the coil of a motor. There are two sets of motor coil, A-phase coil and B-phase coil, and each of them corresponds two poles: positive pole and negative pole. *1
These four poles are placed 90 degrees apart from each other in terms of electrical angles.
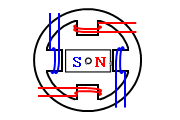 A stepping motor has a structure in which multiple sets of these four poles are lined up. In the above figure, one set of four poles is illustrated. The excitation mode is how you excite and rotate the internal rotor magnet.
A stepping motor has a structure in which multiple sets of these four poles are lined up. In the above figure, one set of four poles is illustrated. The excitation mode is how you excite and rotate the internal rotor magnet.
In the above figure, the magnet rotates 90 degrees, which is the basic angle of one step, and rotates an electric angle of 360 degree by four steps.
The actual motor is: One rotation = 4 steps × the number of pairs.
For example, PF25-48 motor made by NPM has 12 pairs of 4 poles, so 48 is the basic step number.
The division number of one motor rotation is determined by the excitation mode, and there are "2-2-phase excitation /1-2 phase excitation" and "Micro-step" modes.
*1 The coil terminal pins are A phase of the positive pole, A phase of the negative pole, B phase of the positive pole, and B phase of the negative pole.
A phase and A phase of A-phase coil are referred as phase 1 and phase 3, and B phase and B phase of B-phase coil are referred as phase 2 and phase 4.
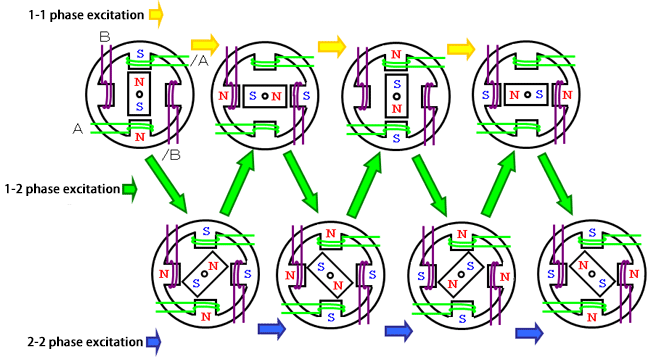
2-2 phase excitation / 1-2 phase excitation
The following excitation modes can be created only by ON/OFF of the motor coil of each phase:
2-2 phase excitation
1-1 phase excitation *2
1-2 phase excitation
1-1 phase excitation and 2-2 phase excitation rotates at an electric angle of 360 degrees in four steps.
1-2 phase excitation doubles resolution by alternating 1-1-phase excitation and 2-2-phase excitation, and a motor rotates one revolution at twice the basic number of steps.
For example, if the motor’s basic step is 48, one rotation will be 96 steps in 1-2 phase excitation. 1-2 phase excitation is often used to reduce the vibration of a motor.
*2 Since 1-1 phase excitation has less torque and damping properties than 2-2-phase excitation, this excitation mode is less used.
Electric angle of 360-degree rotation in 2-2 phase excitation
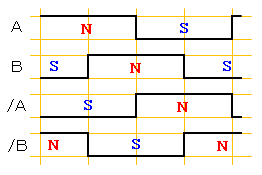 Switch the motor coil current of each phase in a fixed sequence and switch the excitation (N/S polarity) to rotate a motor.
Switch the motor coil current of each phase in a fixed sequence and switch the excitation (N/S polarity) to rotate a motor.
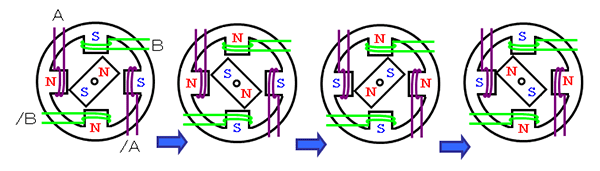
Electric angle of 360-degree rotation in 1-2 phase excitation
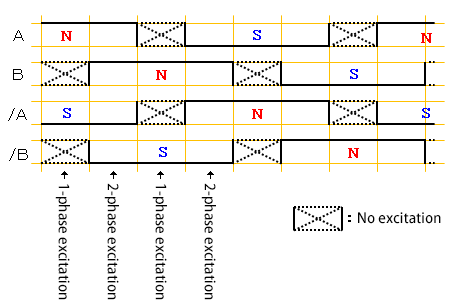 By alternating 1-1 phase excitation and 2-2-phase excitation, the resolution is doubled, which is 1-2 phase excitation.
By alternating 1-1 phase excitation and 2-2-phase excitation, the resolution is doubled, which is 1-2 phase excitation.
Micro-step drive
In addition to ON/OFF of each phase of motor coils, a motor can be stopped at a position finer than the basic step angle by changing the current ratio flowing through A-and B-phase coils. This is called micro-step drive.
Micro-step excitation mode includes W1-2 phase excitation, 2W1-2 phase excitation, 4W1-2 phase excitation, and the like.
W1-2 phase excitation is one rotation at four times of the basic step number.
2W1-2 phase excitation is one rotation at eight times of the basic step number.
4W1-2 phase excitation is one rotation at 16 times of the basic step number.
For example, if the basic step number of a motor is 48, W1-2 phase excitation will rotate 360-degree by 192 steps, 2W1-2 phase excitation by 384 steps, and 4W1-2 phase excitation by 768 steps. *3
*3 Since micro step changes the current ratio, and the rotor stops balanced in the middle of the basic step angle, the stopping position may not be accurate depending on the motor structure. With our PF motors, the micro-step drive is effective to reduce vibration and noise.
For 2-phase excitation
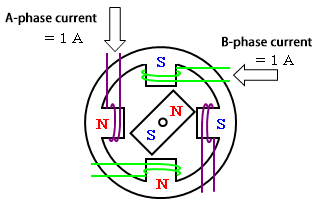 For 2-phase excitation, the current values applying to A and B phases are the same.
For 2-phase excitation, the current values applying to A and B phases are the same.
For micro-step drive
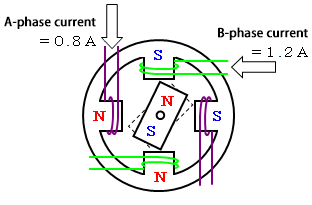 Lower the current to A-phase and higher the current to B-phase in order to increase the force attracted by B-phase coil, so that the magnet is held in the middle.
Lower the current to A-phase and higher the current to B-phase in order to increase the force attracted by B-phase coil, so that the magnet is held in the middle.
In addition to these specifications, drive ICs have various other specifications.
You can drive stepping motors easily by using the drive ICs once you understand the fundamental knowledge.
When designing the actual circuit board, you need to pay attentions not only to the specifications, but also to the current value and heat generation as well as to the routing of grounds and current detection resistors.
Semiconductor companies often provide you the evaluation boards or technical documentation of such drive ICs, so it would be effective to use them.
INDEX
- 1. Fundamentals of stepping motor drive IC
- 2. Specification of the signal that gives operation commands to a drive IC
- 3. Drive IC control method "Excitation mode"
- 4. Decay control
- 5. Current setting when using constant-current drive ICs
- 6. How to select a motor to drive with a constant-current drive IC
- 7. Heat generation of a motor and a driver
- 8. Acceleration and deceleration of stepping motors
- 9. Malfunctions of stepping motors